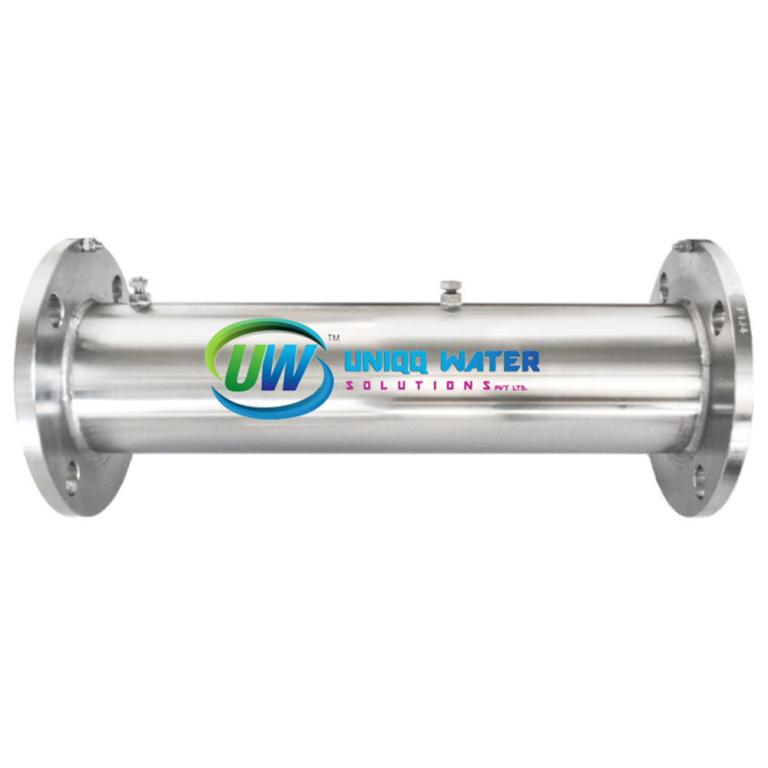
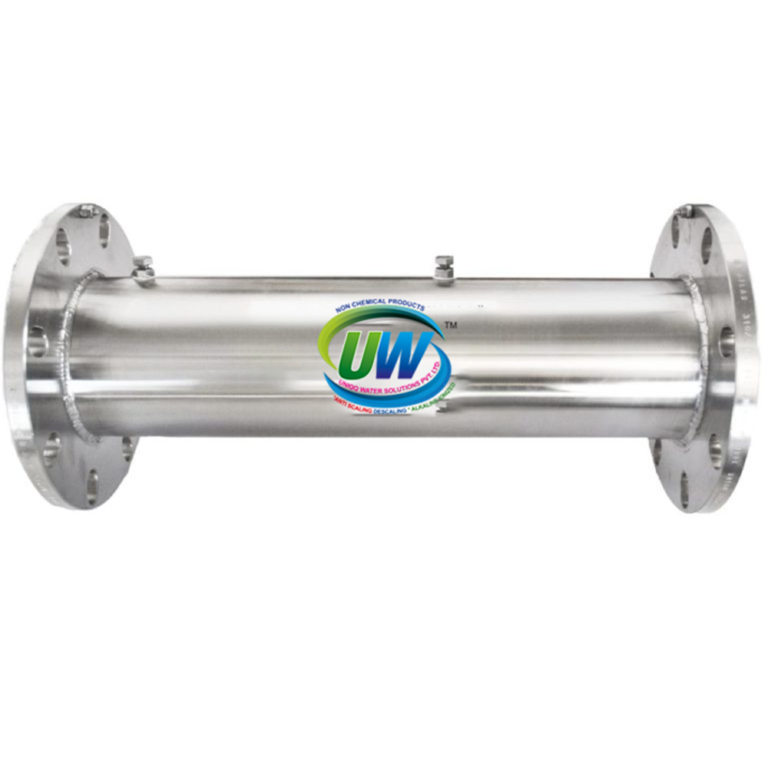
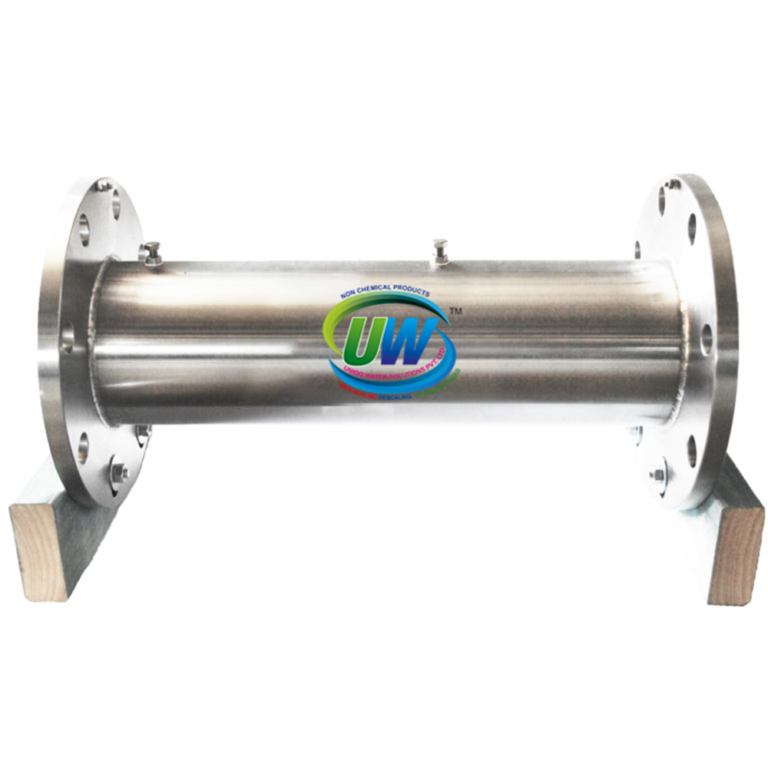
UWS Water Conditioner For Industrial Use
Hard Water Problems In Industrial Sector
The presence of calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions in a water supply is commonly known as “hardness.” The degree of hardness is classified as follows:
The main problem associated with hardness is scale and deposits formation. Even levels as low as 5 to 8 mg/L are too extreme for many uses (i.e. as boiler feed water).
Hardness, and in particular calcium, tend to precipitate coupling with anions like carbonate, phosphate or sulphate. Calcium and magnesium carbonates solubility is in inverse proportion to temperature, which means that as higher the temperature, the lower the solubility is.
Hardness in water is the main source of scale formation in heat transfer equipment, boilers and pipelines:
- It will cause buildup of scale in pipes causing reduced flow and pressure drop increase, then causing greater pumping cost associated, and eventually causing pipes to need to be internally cleaned or replaced.
- Hard water in cooling towers can reduce the effectiveness of heat transfer, causing increased running costs. It can also cause corrosion in the towers, leading to costly repairs or filling replacement of cooling towers.
- In boilers, once scale begins to form on tube surfaces, it creates another layer of material through which heat must pass to get to the water. Two main problems occur due to the insulative effect of the scale material: under deposit corrosion and overheating of the boiler tube metal (creating “hot spots”), leading to water tubes failure and stress corrosion cracking, pushing up operational costs. It also causes the need for more costly maintenance and repairs and will reduce the lifespan of the boiler.
Hence, poor quality of water used in industry is one of the major causes of economic loss due to equipment mechanical failure and maintenance problems. All the above ultimately lead to unplanned turnarounds to make repairs and chemical/mechanical cleanings. Chemical cleaning represents a less expensive option than mechanical cleaning (e.g. hydro-blast). Nonetheless, while the latter typically complete removes the fouling deposits, the effectiveness of chemical cleaning depends on many factors (choice of chemical, deposit composition and ageing, etc.) and often leaves the surface only partially clean.
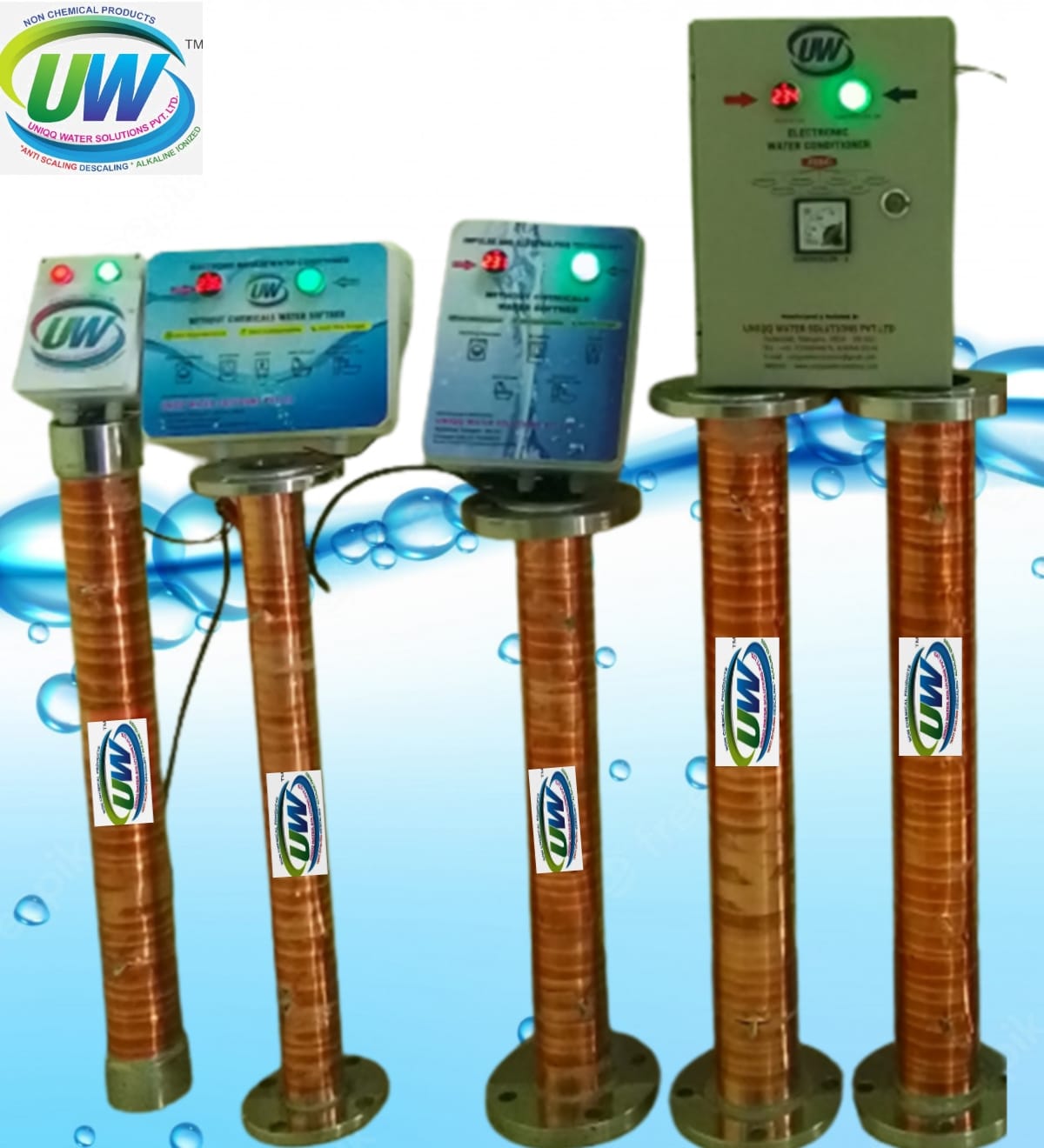


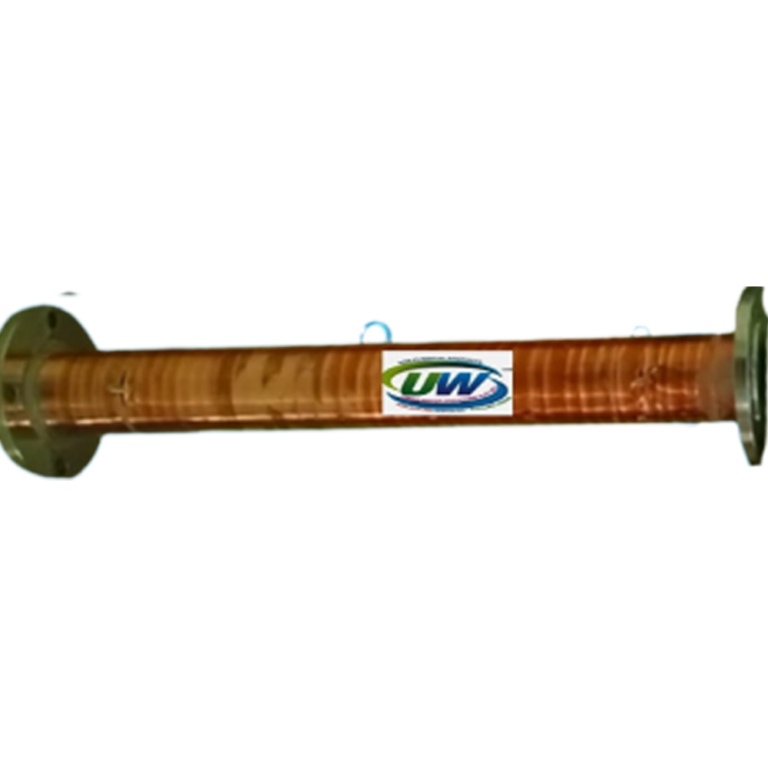
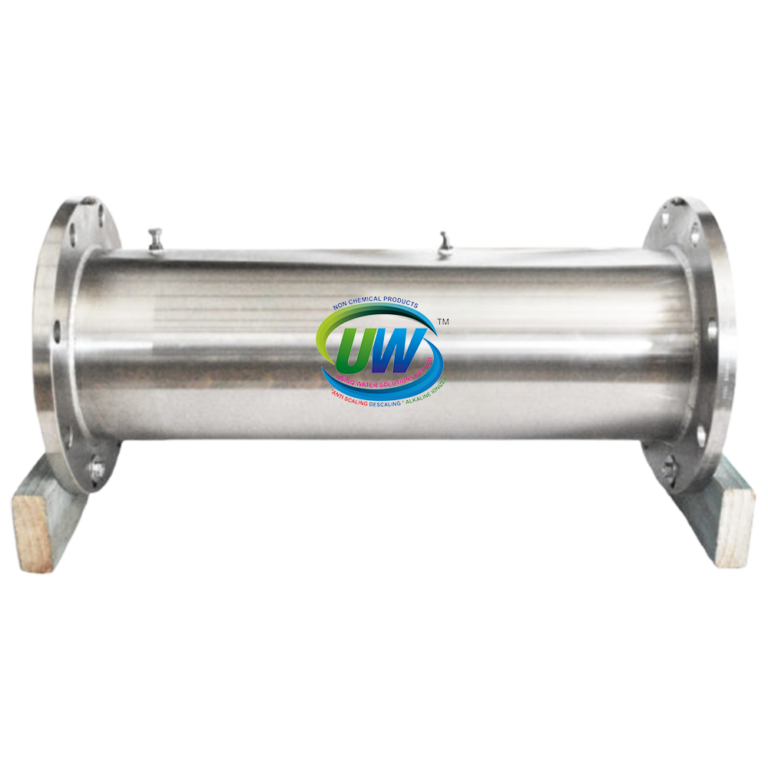
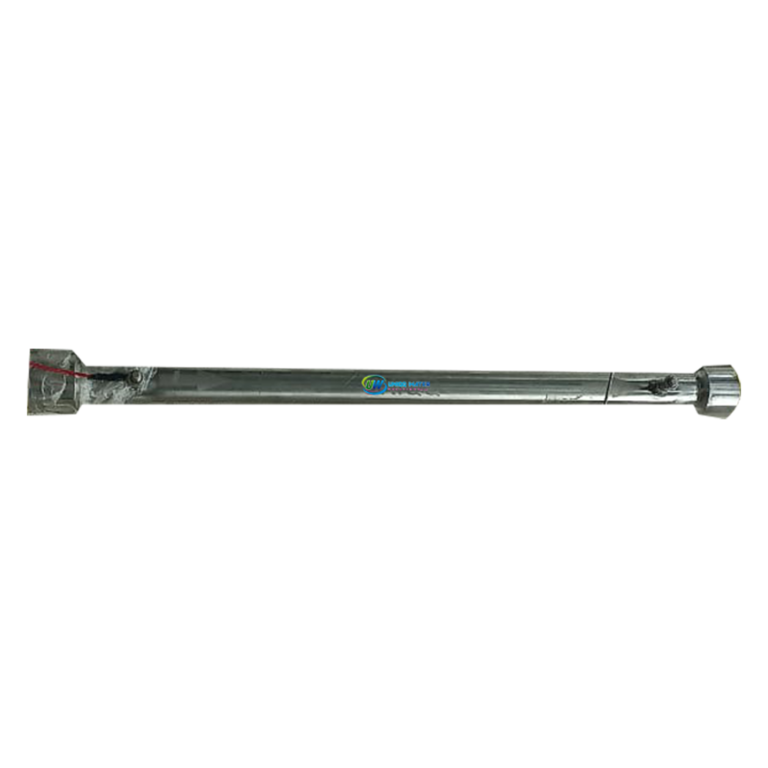
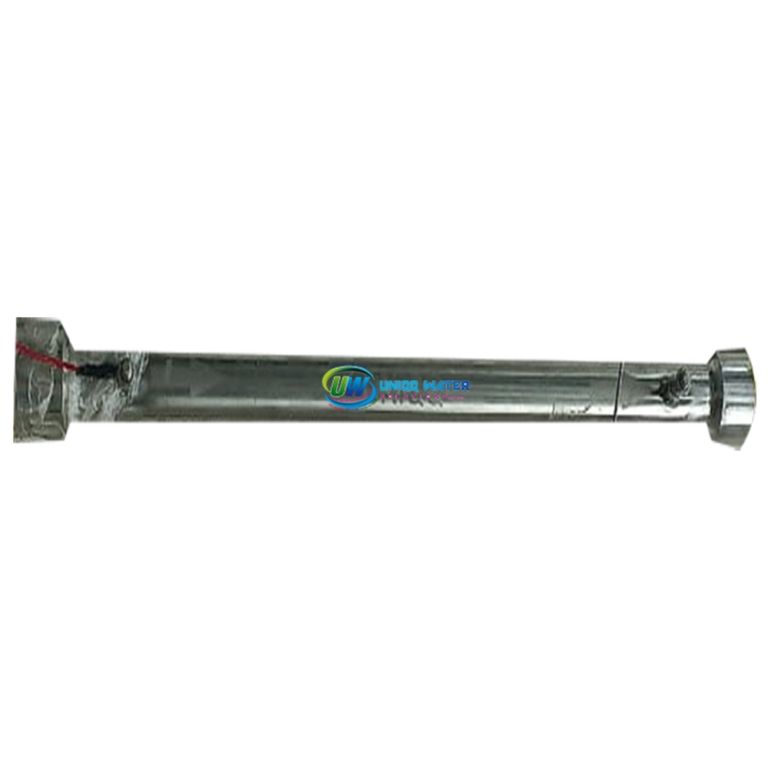
Range Of Sizes To Suit Your Flow Rate
Flow rates: 12 lit/min to 15,300 lit/min
Connection: Threaded or flanged
Length: Various<br
Always pair with an earth kit / power supply
Consider the Benefits
- Saves water by 20 to 30%
- The vegetation period decreases.
- Crop production & crop quality increases.
- Improves soil structure. Controlling PH level.
- Remove and prevent scaling on dripper and sprinkler
- Reduce tip burning problem in leaves upto 45 to 60%
- Increase growth rate of all types of crops & plants by 35 to 40%
- Increase solubility of water for fertilizers, gives 100% benefits of fertilizers,
- Increase oxygen concentration which increase seed germination
- Reduces effect of Chlorides & Fluorides, increases roots efficiency
- Water is absorbed into the ground more easily because of low viscosity.
- Fertilizer and Pesticides are mix very well and it gives better result.
- It clean the root hair and root cap area in the soil.
- Pure form of minerals will be kept in water which help the crops.
- Water absorption becomes more easy for roots and they become healthier.
- Basic nutrients are made available to root zone, it enhances plant growth.
- Reduces effect of Chlorides & Fluorides, increases roots efficiency
- Cleans root hair and root cap area to increase water absorption by roots
- Pipe, Drip irrigation and sprinkler nozzles will be protected from scaling.
- After a month – the number of blocked drippers was declining and The usual
- procedure of cleaning drippers and flushing the lines is not required
APPLICATIONS
There are numerous uses for commercial water softener systems, including applications in the following industries:
- Boilers
- Heat Exchangers
- Cooling Towers
- Chillers
- Evaporative Condensers
- Injection Molding Machines
- Annealing Furnaces
- Reverse Osmosis Systems
• Food and Beverage
• Manufacturing
• Medical
• Pharmaceutical
• Service/Tourism
• Agricultural
• Commercial




Water Conditioner Products
Our Client
Testimonials












